1 Introduction
Well being is outlined as a state of full bodily, psychological, and social wellbeing and never merely the absence of illness and infirmity (1). Well being is likely one of the most simple human rights; it impacts all areas of the life of people. Subsequently, enhancing, defending, and sustaining well being is vital for all people and societies (2, 3). It’s said that human well being (the state of full bodily, non secular, and social wellbeing) is dependent upon life-style (as much as 70%), heredity (15%), surroundings (8%−10%), and medication (8%−10%) (4, 5). Well being promotion is a state of affairs that requires folks to control their existence, maintain the behaviors that have an effect on their well being underneath management, and arrange their each day residing actions by taking accountability for their very own well being with the intention to obtain optimum well being situations (6, 7).
The World Well being Group (WHO) outlined its targets and techniques with the slogan “Well being for All within the 2000s: 21 Objectives within the twenty first Century” on the forty eighth European regional assembly in Copenhagen in 1980. The obvious side of those targets and techniques is the topic of enhancing well being (8, 9). There are three primary methods for enhancing well being: it’s said as establishing primary situations for well being promotion and advocacy, enabling folks to enhance their very own well being, and fostering intersectoral cooperation (3).
Pender (10) outlined the well being promotion mannequin. The principle concept of the mannequin is to create a wholesome life-style to enhance well being. Subsequently, behaviors must be modified to be wholesome. Pender (10) said {that a} wholesome life-style has two features. These are safety and promotion of well being. The well being promotion mannequin was revised by Pender et al. (11). Within the closing model of the mannequin, parts affecting health-changing behaviors had been outlined as “particular person traits and experiences,” “behavior-specific cognitive processes,” and “conduct penalties” (12).
Pender (13) said {that a} wholesome life-style is a part of enhancing well being. A wholesome life-style is the power of the person to regulate behaviors which will have an effect on well being and select behaviors acceptable to their well being standing whereas regulating each day actions. Well being conduct is all of the behaviors that a person believes and practices to remain wholesome and shield in opposition to ailments (14–16). A wholesome life-style for people shouldn’t solely embody safety from ailments but additionally embody behaviors that enhance the extent of wellbeing all through life. Wholesome life-style behaviors comprise non secular improvement, well being accountability, train, diet, interpersonal relationships, and stress administration (17). It will be important for people to amass wholesome life-style behaviors with the intention to stop lifestyle-related ailments and deaths as a consequence of these ailments. Buying these behaviors is vital for stopping persistent ailments, enhancing the standard of life within the presence of persistent ailments, and selling wholesome getting older (18).
You will need to acquire correct details about well being and have acceptable abilities in making selections about conditions which will have an effect on people’ well being with the intention to develop wholesome life-style behaviors (19). Not doing sufficient bodily exercise, not having an satisfactory and balanced weight loss program, and utilizing addictive substances (cigarettes, alcohol, and many others.) and health-threatening behaviors are liable for a lot of the ailments and deaths related to persistent ailments (20). In keeping with the worldwide burden of illness research, 34.1 million folks died as a consequence of preventable danger elements in 2017. One of many 5 dangers that triggered loss of life in 2017 was smoking, and the opposite was excessive physique mass index (BMI) (21). The American Middle for Illness Management (CDC) reported that if folks exhibit a number of wholesome life-style behaviors, their life expectancy can be prolonged (22).
In keeping with statistics from the World Well being Group, 70%−80% of deaths in developed international locations and 40%−50% in underdeveloped international locations are brought on by ailments that happen as a consequence of life-style (23, 24). In keeping with the Nationwide Burden of Illness and Value Effectiveness Mission knowledge, it’s said that an important causes of loss of life in Turkey are ischemic coronary heart ailments, cerebrovascular ailments, and persistent obstructive pulmonary illness. An individual’s personal perspective and conduct play a significant function within the formation of those non-communicable ailments (25).
Good well being boosts profitable studying. The wellbeing of each pupil is of utmost significance and is a primary side of an environment friendly schooling. Way of life immediately impacts the wellbeing of scholars. Lecturers are a major agent in empowering college students with abilities for wellbeing and wholesome residing (26).
In keeping with WHO (27), faculties ought to implement health-promoting insurance policies and practices, comparable to making a wholesome psychosocial surroundings for college kids and employees, equal therapy for all college students, insurance policies on drug and alcohol use, tobacco use, first support, and violence that assist stop or cut back bodily, social, and emotional issues.
In Turkey, Article 1 of the Main Schooling and Coaching Legislation No. 222 defines major schooling as an establishment that serves the bodily, psychological, and ethical improvement and upbringing of scholars. It’s doable to attain this aim by offering a wholesome and protected schooling and coaching surroundings (28). Taking mandatory precautions for college kids to amass data, abilities, and habits concerning cleanliness, well being, and diet is included within the primary legal guidelines of major schooling (29).
Lecturers’ behaviors and persona traits have an effect on college students’ behaviors and persona traits. On this case, lecturers with completely different personalities have completely different results on their college students. The behaviors of major faculty lecturers within the classroom have an effect on the scholars’ success within the lesson. An efficient and environment friendly trainer is one who is just not solely an knowledgeable in his or her area at a excessive stage but additionally one who can adequately clarify these competencies to his or her college students; in different phrases, one who supplies efficient studying and instills behavioral habits. Bodily activity-related abilities are among the many data, abilities, and attitudes that major faculty lecturers ought to have in topics comparable to schooling, scientific methodology, anatomy, physiology, psychology, and well being. This helps the first faculty trainer contribute to the versatile improvement of scholars (30).
At school well being providers, which embody all of the work to be performed to judge and enhance the well being of scholars and faculty personnel to make sure a wholesome faculty life and thus to create a wholesome society, particularly lecturers being an excellent mannequin to college students with their very own conduct types the premise for shaping the longer term lives of scholars by influencing their conduct (31, 32). Nevertheless, faculties that put together people for all times and educate them to develop optimistic behaviors may mediate the event of unfavorable behaviors. Unhealthy behaviors acquired in childhood proceed in maturity and put the particular person’s well being in danger sooner or later (33).
Research most frequently bear in mind such life-style habits as bodily exercise, weight loss program, smoking, and hours of sleep (33–36). Many adults typically fail to be good function fashions when they should exhibit a wholesome and balanced life-style (37). When it appears to be like on the research on lecturers, in Ak et al. (38) research, 88.8% of lecturers smoked in school, in Tokuç and Berberoglu (33) research, the bottom common of health-promoting behaviors was within the train dimension, in Gürel et al. (39) research, 80.9% of lecturers have insufficient diet data. Within the research carried out by Kabataş et al. (40) with feminine lecturers, it was decided that 17.6% of the lecturers had been overweight. Research on wholesome life-style behaviors in Turkey present that there are vital issues. Though many authorized laws and requirements have been developed concerning wholesome residing in faculties, it’s noticed that deficiencies and issues associated to wholesome residing in faculties proceed in Turkey. With the intention to develop wholesome life-style behaviors in major faculties, it’s essential to know the opinions of related folks and organizations concerning wholesome existence.
Because of the literature evaluate on wholesome life-style behaviors, it’s seen that analysis within the area of schooling in Turkey is generally carried out on well being employees, college students in faculties offering well being schooling, trainer candidates, academicians, and lecturers. Whereas research on this area in Turkey have been utilized to completely different areas, not many research have been carried out on major faculty lecturers. Because of this, research on this area will function a useful resource for future research.
Lecturers have vital roles and obligations in growing and sustaining wholesome life-style behaviors amongst people in society. Because of this, lecturers must have data and consciousness about well being and rework this consciousness and data into attitudes and behaviors (41). Nevertheless, the outcomes of analysis carried out in Turkey and different international locations present that lecturers’ wholesome life-style behaviors are usually not but on the desired stage (33, 37, 42–49). Moreover, when the literature is considered there are lots of research utilizing the “Well being-Promotion Way of life Profile Scale” in Turkey and different international locations. When these research are evaluated, it’s noteworthy that there are research masking all kinds of subjects, from adolescent moms (50), to older grownup girls (51), from persistent illness prevention packages (52), to high quality of life in persistent ailments (53, 54), to the analysis of wholesome life-style behaviors of scholars (55, 56), adults (57), and employees (58, 59). Nevertheless, research carried out on lecturers are fairly restricted. It’s thought that this research will partially get rid of the present deficiency.
It’s said that values associated to life and well being are acquired at an early age, that major faculty lecturers have a decisive function on this regard, and that they affect the rise of the final wellbeing stage of scholars and the unfold of wellbeing with the schooling they supply and the optimistic behaviors they present (60). In gentle of this info, the issue of this analysis is to find out the extent of well being promotion life-style behaviors of lecturers working in major faculties and in addition to look at whether or not socio-demographic traits impact their well being promotion life-style behaviors.
1.1 Function of the analysis
The goal of the present research was to find out the degrees of wholesome life-style conduct amongst lecturers working in public major faculties. As well as, it was aimed to find out the consequences of some chosen variables (gender, marital standing, taking programs on well being promotion, following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media) on wholesome life-style behaviors. Solutions had been requested for the next questions:
1. What are the socio-demographic traits (gender, marital standing, taking programs on well being promotion, following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media) of the lecturers taking part within the analysis?
2. What’s the stage of health-promotion life-style profile (HPLP-II) scale amongst lecturers working in public major faculties?
3. What are the traits affecting the health-promotion life-style behaviors amongst lecturers?
(a) Does the extent of lecturers’ health-promotion life-style behaviors differ in keeping with their gender?
(b) Does the extent of lecturers’ health-promotion life-style behaviors differ in keeping with their marital standing?
(c) Does the extent of lecturers’ health-promotion life-style behaviors differ in keeping with their taking programs on well being promotion?
(d) Does the extent of lecturers’ health-promotion life-style behaviors for six parts differ in keeping with their following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media?
2 Supplies and strategies
2.1 The mannequin of the analysis
The current research was designed utilizing a survey mannequin. The survey mannequin is a analysis strategy that goals to explain a previous or current state of affairs or occasion because it exists (61).
2.2 Inhabitants and pattern
The inhabitants of the present research comprised of lecturers (N = 372) working in numerous branches in 15 public major faculties in Amasya metropolis middle in Turkey within the spring time period of the 2018–2019 tutorial yr. Amasya is a metropolis, a area in Turkey consisting of round 341.000 inhabitants. All included faculties had been state-funded, because the overwhelming majority of faculties in Turkey are state funded. The analysis pattern consisted of all members of the inhabitants. 300 fifty lecturers had been reached as a consequence of causes comparable to not agreeing to take part within the analysis, being on go away, sick, and offering incomplete solutions to the surveys on the dates the analysis was carried out. A complete of 350 completed questionnaires had been returned and analyzed. The comfort sampling method was used. The info was collected by the researcher, utilizing face-to-face interview methods within the faculty surroundings between June 19 and July 17, 2018.
2.3 Information assortment instruments
A Well being-Promotion Way of life Profile (HPLP-II) Questionnaire and a private attribute kind had been carried out to establish the extent of well being promotion life-style behaviors amongst lecturers. The private info kind was a four-item questionnaire. It was purposed at figuring out the sociodemographic traits of contributors: gender, marital standing, taking programs on well being promotion, and following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media. The instrument of the current research, titled “Well being-Promotion Way of life Profile (HPLP-II) Scale,” was initially developed by Walker and Hill-Polerecky (62) and tailored to Turkish by Bahar et al. (63). The questionnaire measures health-promoting behaviors associated to an individual’s wholesome life-style. It’s a questionnaire whose validity and reliability have been confirmed in functions made on completely different populations.
This scale consists of 52 gadgets masking six subscales: well being accountability (9 gadgets), bodily exercise (eight gadgets), diet (9 gadgets), non secular development (9 gadgets), interpersonal relations (9 gadgets), and stress administration (eight gadgets). The questionnaire was offered to contributors who answered utilizing a four-point Likert-type scale starting from 1 “by no means” to 4 “routinely” (1 = by no means, 2 = generally, 3 = typically, or 4 = routinely). The utmost level obtainable from the general HPLP-II scale is 208. The minimal level obtainable on the general HPLP-II scale is 52. The bottom and highest factors that may be obtained from the subscales are: 9–36 for non secular development, 9–36 for well being accountability, 8–32 for bodily exercise, 9–36 for diet, 9–36 for interpersonal relationships, and eight–32 for stress administration. As the purpose obtained from the size will increase, the person’s stage of implementation of the required well being behaviors will increase. All gadgets on the size are optimistic; there aren’t any reverse gadgets. The factors within the subgroups can be utilized independently. The entire level of all subgroups of the size offers the wholesome life-style behaviors rating (63).
It was discovered that the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was 0.94 for the overall scale. The Cronbach Alpha inner consistency coefficients starting from 0.79 to 0.87 had been reported for the subscales (62). The Cronbach Alpha reliability coefficient of the size by Bahar et al. (63) was discovered to be 0.92. The Cronbach Alpha coefficient was calculated to check the reliability of the measurements of this analysis for every sub-scale which was discovered to be 0.729 for the sub-scale of “well being accountability,” 0.839 for the sub-scale of “bodily exercise,” 0.707 for the sub-scale of “diet,” 0.836 for the sub-scale of “non secular development,” 0.821 for the sub-scale of “interpersonal relations,” and 0.707 for the sub-scale of “stress administration.” It has been said that the reliability coefficient on a Likert-type scale must be >0.70 (64).
2.4 Evaluation of the info
On this analysis, the SPSS-22.0 package deal program was carried out to investigate the info. Descriptive statistics comparable to frequency and share had been used to investigate the info offered from the demographic traits of the lecturers taking part within the analysis. As well as, descriptive statistics comparable to imply, customary deviation, frequencies, minimal, and most factors had been calculated for the wholesome promotion life-style profile II subscales. To look at whether or not the info had been usually distributed, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov take a look at and the Shapiro-Wilks take a look at had been carried out. The outcomes indicated that it isn’t usually distributed (p < 0.05) (65). To verify if the distribution of factors was regular, it was calculated on the values of skewness and kurtosis. The kurtosis and skewness coefficients are 0 in a standard distribution (66). Within the current research, the skewness take a look at worth was 2.86, whereas the kurtosis take a look at worth was 0.19. For the reason that knowledge didn’t point out a standard distribution, the non-parametric checks had been carried out. The statistical significance stage for the p-value was set as 0.05.
3 Outcomes
The socio-demographic traits of the respondents are proven in Desk 1. 60.86% of the lecturers answering the analysis are girls, and 39.14% are males. Nearly the entire lecturers (91.71%) had been married. The speed of lecturers who didn’t take a course in pre-service coaching on well being promotion is 66.86%, and the speed of those that took a course is 33.14%. When the standing of following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media is examined, the speed of lecturers who are usually not in any respect is 9.43%, those that have an interest after they have the chance are 37.14%, those that have an interest when mandatory are 26.86%, those that are consistently are 23.43%, and people who have an interest as a consequence of their career are 3.14%.
Desk 1. Contributors’ sociodemographic traits.
In Desk 2, the common whole factors of the well being promotion life profile (HPLP-II) had been 129.93 (SD 19.91), indicating that the well being promotion life behaviors of the lecturers had been medium stage. The sub-dimension common factors of the well being promotion life-style profile scale are respectively: “non secular development” subscale imply rating is 26.52 (SD 4.80), “interpersonal relations” subscale imply rating is 25.38 (SD 4.60), “diet” subscale imply rating is 21.73 (SD 3.90), “well being accountability” subscale imply rating is 20.80 (SD 4.06), “stress administration” subscale imply rating was 19.37 (SD 3.65) and “bodily exercise” subscale imply rating was 16.45 (SD 4.93). In keeping with the subscales, “non secular development” indicated the best common level of 26.52 (SD 4.80), whereas “bodily exercise” indicated the bottom common level of 16.13 (SD 4.76).
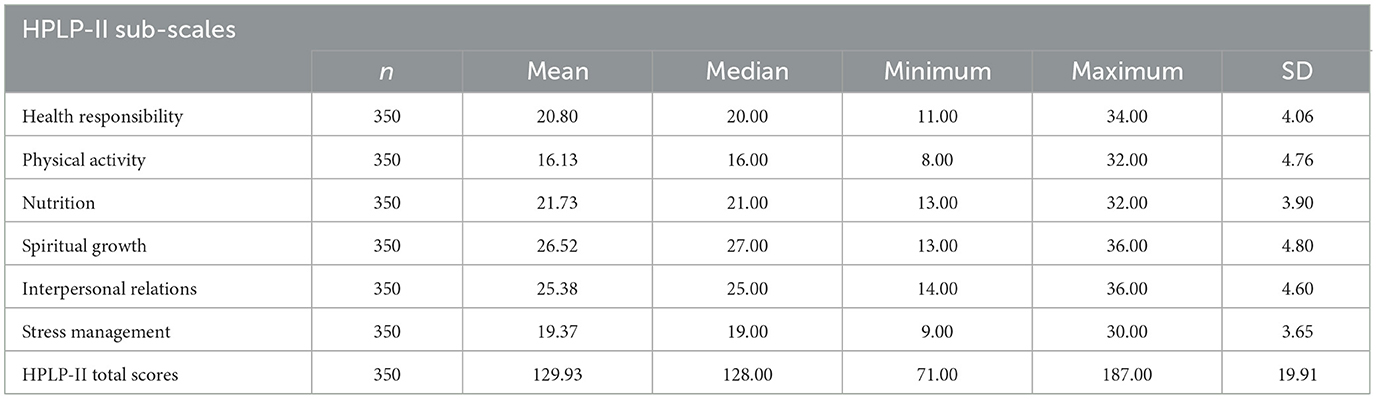
Desk 2. Imply, median, minimal, most, and customary deviation of the Well being Promotion Way of life Profile II (HPLP-II) scale and subscales.
Desk 3 exhibits that there was not important distinction between genders and well being promotion life-style conduct scores. Nevertheless, the overall imply rating of male lecturers obtained for well being promotion life-style was discovered to be 128.64, which was statistically considerably decrease than the imply level of feminine lecturers (130.58), Z = −1.89, p > 0.05, r = 0.1. This represents a small impact measurement for the gender knowledge (66).

Desk 3. Mann–Whitney U-test outcomes of lecturers’ wholesome life-style behaviors II (HPLP-II) scores relying on the their gender variable.
A statistically important distinction was discovered between genders and well being accountability subscale factors (p < 0.05). The well being accountability imply level of male lecturers was discovered to be 20.40, which was considerably decrease than the imply level of feminine lecturers (M = 21.05, Z = −2.345, p < 0.05, r = 0.12). This represents a small impact measurement for the gender knowledge (66) (Desk 3). In keeping with these outcomes, it may be mentioned that gender has an impression on factors of the well being accountability subscales of wholesome promotion life-style behaviors.
When the wholesome promotion life-style behaviors subscales had been investigated, a statistically important distinction was discovered between genders and lecturers’ bodily exercise subscale scores (p > 0.05). Nevertheless, the bodily exercise common level of feminine lecturers was discovered to be 15.70, which was considerably decrease than the common level of male lecturers (M = 16.86, Z = −1.865, p > 0.05, r = −0.09). This represents a small impact measurement for the gender knowledge (66) (Desk 3).
A statistically important distinction was discovered between genders by way of interpersonal relations subscale factors (p < 0.05). The interpersonal relations common level of male lecturers was discovered to be 24.63, which was considerably decrease than the imply rating of feminine lecturers (M = 25.80, Z = −2.681, p < 0.05, r = 0.14). This represents a small impact measurement for the gender knowledge (66) (Desk 3). In keeping with these outcomes, it may be mentioned that gender has an impression on scores of the interpersonal relations subscales of well being promotion life-style behaviors.
There was not statistically important distinction between the genders by way of their factors within the “diet” (M = 21.71, Z = −1.862, p > 0.05, r = 0.09), “non secular development” (M = 26.48, z = 0.81, p > 0.05, r = 0.04), and “stress administration” subscales (M = 19.34, z = 1.402, p > 0.05, r = 0.07; Desk 3).
In Desk 4, there was not important distinction between the well being promotion life-style behaviors scale and subscale scores and marital standing (p > 0.05). In different phrases, whether or not the lecturers taking part within the analysis had been married or single didn’t make a distinction on the wholesome life-style conduct factors. In keeping with these findings, it may be mentioned that marital standing has not impression on factors of the interpersonal relations subscales.
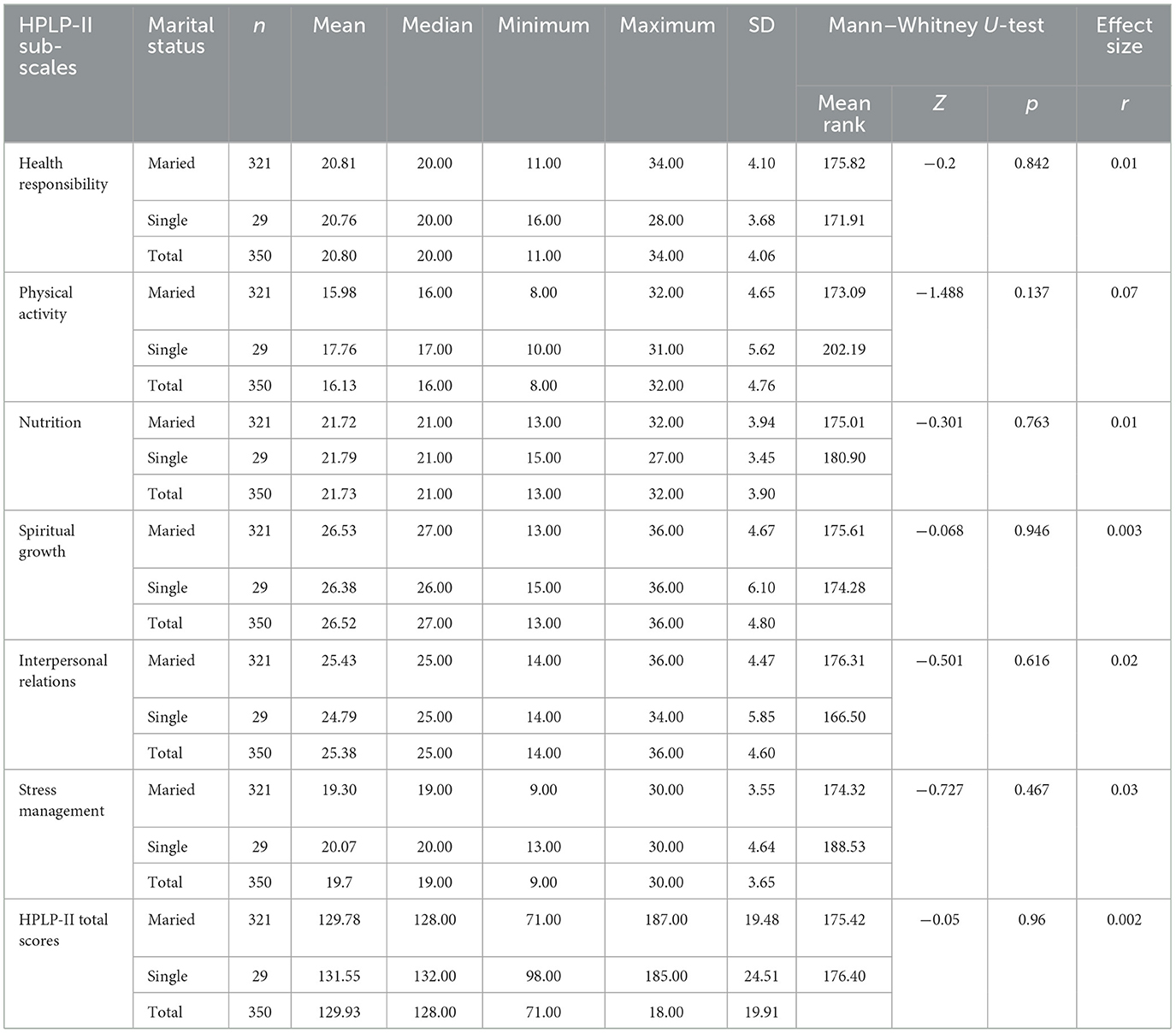
Desk 4. Mann–Whitney U-test outcomes of lecturers’ wholesome life-style behaviors II (HPLP-II) scores relying on their marital standing variable.
Desk 5 exhibits that, there was a statistically important distinction between taking programs on subjects associated to well being promotion and the well being promotion life-style behaviors scale (Mdn = 128.00, p < 0.05, Z = −4.065, r = 0.21). It was decided that the overall imply level of lecturers who took programs on well being promotion (M = 136.17) was increased than the imply rating of lecturers who didn’t take programs (M = 126.83). This represents a small impact measurement (66). In keeping with these outcomes, it may be mentioned that taking programs on subjects associated to well being promotion has an impact on scores of well being promotion life-style behaviors.
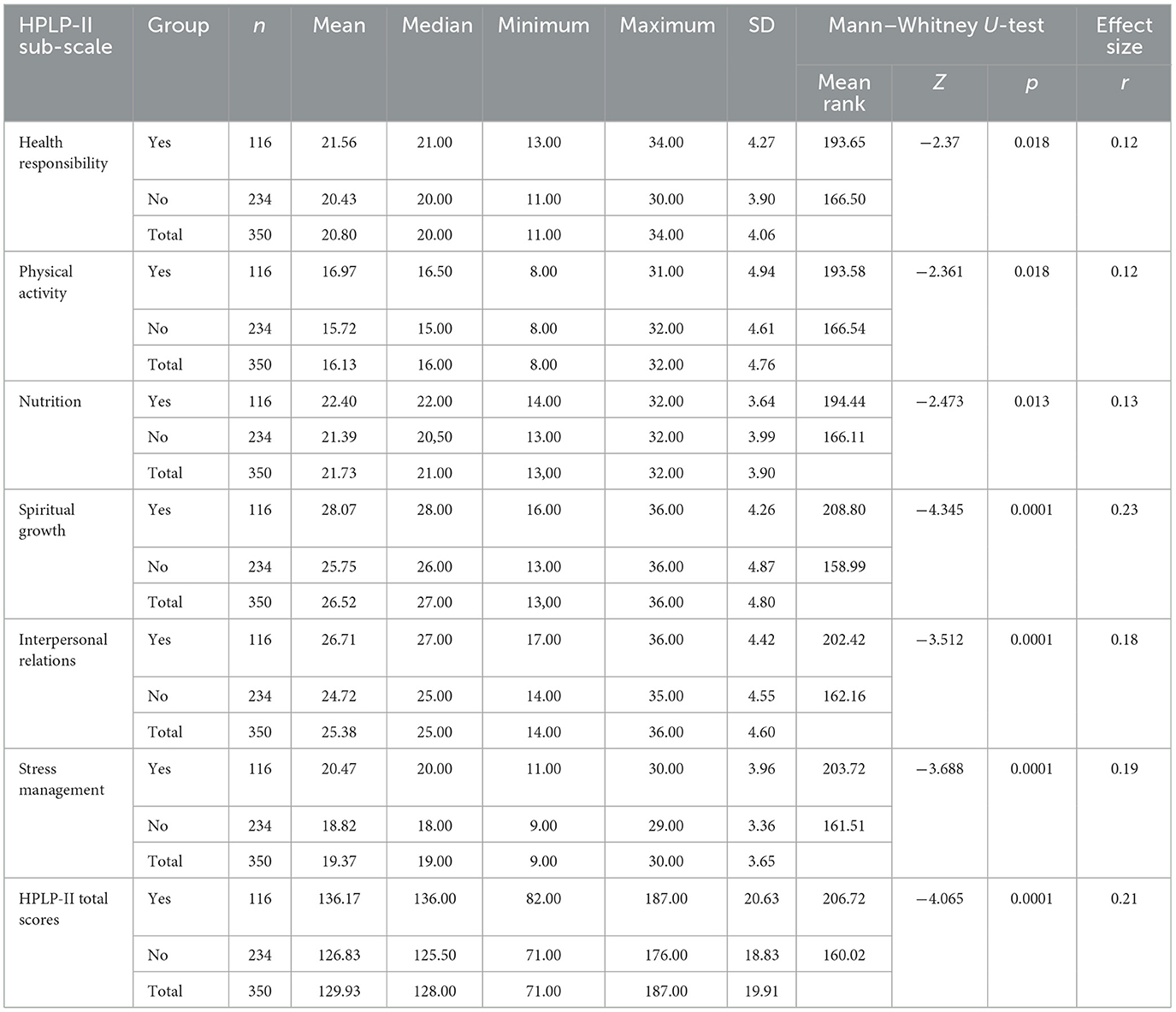
Desk 5. Mann–Whitney U-test outcomes of lecturers’ wholesome promotion life-style behaviors II (HPLP-II) scores relying on their taking programs associated to well being promotion.
When the wholesome promotion life-style profile II sub-scales had been analyzed, a statistically important distinction was discovered between taking programs associated to well being promotion and the “well being accountability” sub-scale factors (p < 0.05). The “well being accountability” imply level of lecturers who took programs on well being promotion throughout their schooling (M = 21.56) was statistically considerably increased in comparison with the rating of the lecturers who didn’t take programs (M = 20.43, Z = −2.37, p < 0.05, r = 0.12). This provides a small impact measurement (66). In keeping with these outcomes, it may be mentioned that taking programs associated to well being promotion has an impact on factors of the well being accountability subscales of wholesome promotion life-style behaviors.
There was a major distinction between taking programs associated to well being promotion and “bodily exercise” sub-scale factors (p < 0.05). The “bodily exercise” imply level of lecturers who took programs on well being promotion points (M = 16.97) was statistically considerably increased in comparison with the purpose of lecturers who didn’t take programs (M = 15.72), z = −2.361, p < 0.05, r = 0.12 (Desk 5). This provides a small impact measurement (66).
There was a major distinction between taking programs on well being promotion and the “diet” subscale level (p < 0.05). The “diet” common level of lecturers who didn’t take programs on well being promotion (M = 21.39) was decrease than the common level of lecturers who took programs (M = 22.40), z = −2.473, p < 0.05, r = 0.13 (Desk 5). This provides a small impact measurement (66).
There was a major distinction between non secular development subscale rating averages and taking programs on well being promotion topics (p < 0.05). The “non secular development” dimension imply rating of lecturers who didn’t take programs on well being promotion (M = 25.75) was considerably decrease than the imply level of lecturers who took programs (M = 28.07), z = −4.345, p < 0.05, r = 0.23; Desk 5). This provides a small impact (66).
There was a major distinction between taking programs on well being promotion topics and the “interpersonal relations” subscale imply rating (p < 0.05). The imply rating of the interpersonal relations dimension of lecturers who didn’t take programs on well being promotion (M = 24.72) was considerably decrease than the scores of lecturers who took programs (M = 26.71, z = −3.512, p < 0.05, r = 0.18; Desk 5). This provides a small impact (66).
There was a major distinction between taking programs on well being promotion topics and stress administration subscale factors (p < 0.05). The “stress administration” imply level of lecturers who didn’t take programs on well being promotion topics (M = 18.82) was considerably decrease in comparison with the imply level of lecturers who took programs (M = 20.47), z = −3.688, p < 0.05, r = 0.19; Desk 5). This provides a small impact (66). Primarily based on these findings, it may be mentioned that taking programs on well being promotion topics has an impact on the entire subscales of the well being promotion life-style conduct scores of the lecturers.
When Desk 6 is examined, there’s a important distinction between the standing of following wholesome life-style packages and articles in written and visible media by way of well being promotion life-style profile scale factors (H = 50.153, SD = 19.91, p < 0.05, r = 0.14). The typical rating of lecturers who had been by no means considering packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media 122.09 (SD 23.33) was considerably decrease in comparison with the purpose of those that had been after they had the chance 124.28 (SD 16.56), when mandatory 128.43 (SD 17.78), all the time 141.85 (SD 17.95), and by career 144.09 (SD 31.24; Desk 6). Primarily based on these findings, it may be mentioned that following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media has an impact on lecturers’ well being promotion life-style profile factors.
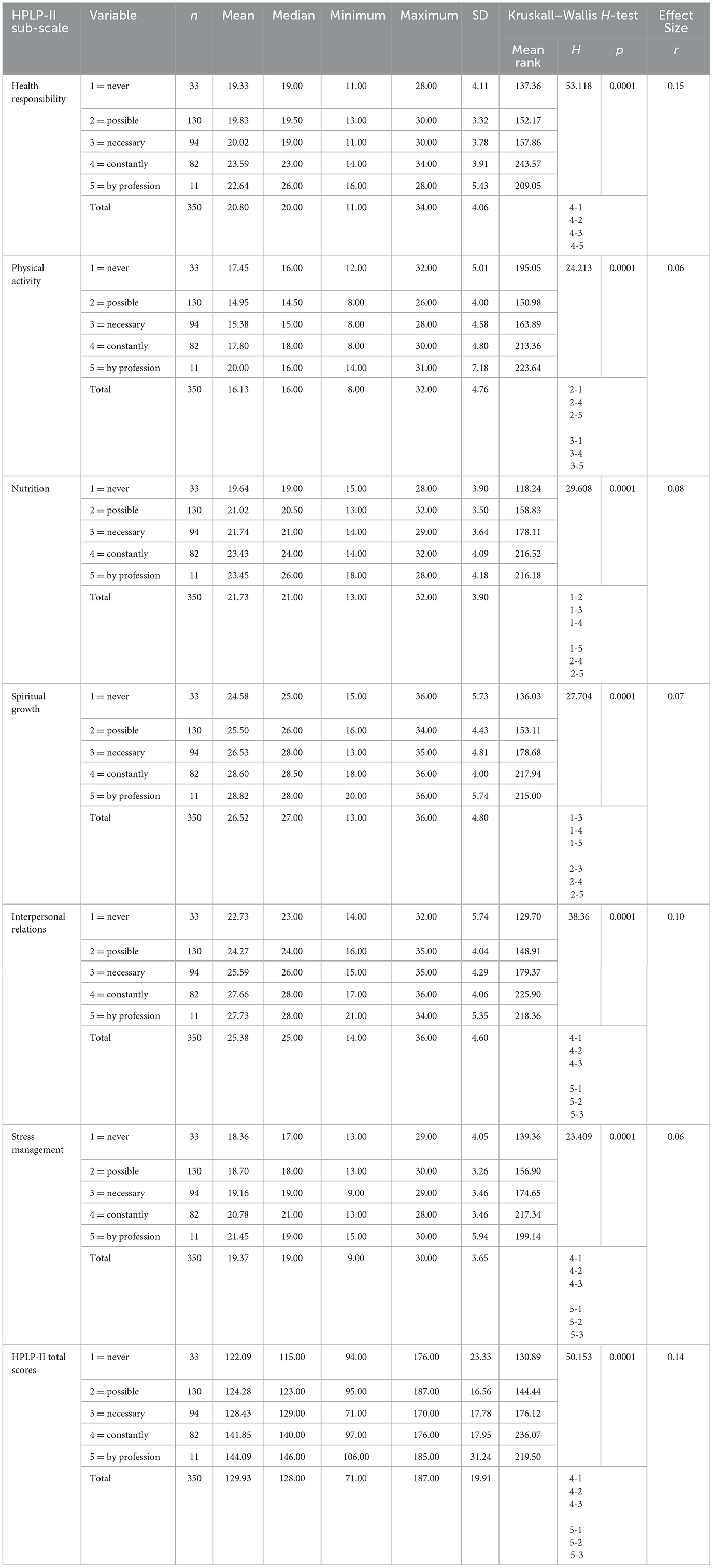
Desk 6. Kruskal–Wallis H-test outcomes of lecturers’ Well being Promotion Way of life Profile II (HPLP-II) scale and subscale scores relying on their following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media.
A statistically important distinction was revealed between the “bodily exercise” dimension subscale level common of the lecturers taking part within the research and their standing of following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media (H = 24.213, SD = 4.76, p < 0.05, r = 0.06). When the common bodily exercise subscale rating of the lecturers answering within the analysis was in contrast with their standing of following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media: by no means 17.45 (SD 5.01), those that had been every time doable 14.95 (SD 4.00), those that had been when mandatory 15.38 (SD 4.58, p < 0.05), those that had been consistently 17.80 (SD 4.80), and people who had been considering their career 20.00 (SD 7.18) subscale factors, a major distinction was revealed between the averages (Desk 6). Primarily based on these findings, it may be mentioned that following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media has an impact on lecturers’ bodily exercise subscale scores.
A big distinction was revealed between the “diet” dimension subscale level common of the lecturers answering within the research and their standing of following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media (H = 29.608, SD = 3.90, p < 0.05). The diet dimension subscale rating common of lecturers who by no means comply with packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media was 19.64 (SD 3.9); those that comply with them after they have the chance had been 21.02 (SD 3.50); those that comply with them when mandatory had been 21.74 (SD 3.64); and people who comply with them consistently had been 23.43 (SD 4.09); and as a consequence of their career 23.45 (SD 4.18; Desk 6). Subscale factors confirmed a statistically important distinction between the averages. Primarily based on these findings, it may be mentioned that following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media has an impact on lecturers’ “diet” subscale rating.
A big distinction was revealed between the “non secular development” subscale imply rating of the lecturers taking part within the analysis and their following of packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media (H = 27.704, SD = 4.80, p < 0.05). The non secular development imply rating of those that by no means comply with packages and articles about wholesome residing was 24.58 (SD 5.73), the imply rating of those that comply with them after they have the chance was 25.50 (SD 4.43) and when mandatory was 26.53 (SD 4.81), the rating of those that comply with them consistently was 28.60 (SD 4.00), and as a consequence of their career was 23.45 (SD 4.18) subscale factors. A big distinction was revealed between the averages (Desk 6). Primarily based on these findings, it may be mentioned that following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media has an impact on lecturers’ “non secular development” subscale rating.
There was a major distinction between the “interpersonal relations” subscale level of the lecturers taking part within the analysis and their following of packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media (H = 38.36, SD = 4.60, p < 0.05, r = 0.10). The non secular development imply rating of those that by no means comply with packages and articles about wholesome residing was 22.73 (SD 5.74), the imply rating of those that comply with them after they have the chance was 24.27 (SD 4.04) and when mandatory was 25.59 (SD 4.29), the rating of those that comply with them consistently was 27.66 (SD 4.06), and as a consequence of their career 27.73 (SD 5.35; Desk 6). The subscale factors confirmed a major distinction between the averages. Primarily based on these findings, it may be mentioned that following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media has an impact on lecturers’ “interpersonal relations” subscale rating.
There was a major distinction between the stress administration subscale factors of the lecturers taking part within the research and their following of packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media (H = 23.409, SD = 3.65, p < 0.05, r = 0.06). The stress administration imply rating of those that by no means comply with packages and articles about wholesome residing was 18.36 (SD 4.05), the imply rating of those that comply with them after they have the chance was 18.70 (SD 3.26) and when mandatory was 19.16 (SD 3.46), the rating of those that comply with them consistently was 20.78 (SD 3.46), and as a consequence of their career 21.45 (SD 5.94; Desk 6). The subscale factors confirmed a major distinction between the averages. Primarily based on these findings, it may be mentioned that following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media has an impact on lecturers’ “stress administration” subscale rating.
4 Dialogue
The aim of this analysis was to find out the degrees of well being promotion life-style conduct amongst lecturers. As well as, the current research examined whether or not well being promotion life-style behaviors differ in keeping with chosen socio-demographic traits comparable to gender, marital standing, taking programs on well being promotion, and following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media.
On this research, it was discovered that the general rating of lecturers on the well being promotion life-style behaviors questionnaire was at a medium stage. The utmost rating that may be obtained from the well being promotion life-style behaviors questionnaire is 208, and the common well being promotion life-style behaviors rating within the current research was discovered to be 129.93. In step with this consequence, it’s recommended that the well being promotion life-style behaviors of the contributors must be supported. In some research carried out in Turkey, the common wholesome life-style conduct scores had been 122.1 ± 19.8 (67), 125.9 ± 17.4 (68), 134.5 ± 17.9 (33), 128.74 ± 18.24 (69), and 144.90 ± 24.07 (70). It has been discovered that the common rating of bodily schooling lecturers’ wholesome life-style conduct was 145.7 ± 15.5 (71). Kaya et al. (72) said that the final rating of school lecturers on health-promoting life-style behaviors was 139.5 ± 18.0, which was discovered to be increased than this research. In a research carried out by Çebi (73) to find out the wholesome life-style behaviors of athletes, the overall factors of the athletes on the wholesome life-style conduct scale had been discovered to be 135.74 ± 21.46. In research carried out with the identical scale in different international locations, well being promotion life-style behaviors imply scores had been discovered to be decrease (58). Rahnavard et al. (74) discovered that an undesirable life-style was detected in 50% of the lecturers. Pirzadeh et al. (47) said that 23% of lecturers had a reasonably wholesome life-style. Within the research carried out by Seema (26) on lecturers working in secondary faculties, the common worth of wholesome life-style behaviors was revealed to be 135.9.
Well being promotion life-style behaviors within the present analysis had been analyzed concerning six dimensions. Relating to the findings of the six dimensions, it has been seen that the best common level share of well being promotion life-style behaviors was discovered for lecturers responses to non secular development part adopted by the interpersonal relationships part, whereas lecturers’ well being promotion life-style to bodily exercise dimension was the bottom. The subscale signifies that lecturers want help in bodily exercise abilities. The excessive non secular development rating of the lecturers taking part within the analysis might be interpreted as their feeling of worth and self-appreciation. This case is extraordinarily vital for the event of the career. Many research might be discovered within the literature with related findings to the present research. It was discovered that the contributors acquired the best common level within the non secular improvement sub-scale and the bottom imply level within the bodily exercise sub-scale (2, 37, 75–81). In another research, it was discovered that the best imply level of the contributors was within the interpersonal relations sub-scale, the bottom rating was within the bodily exercise sub-scale (82–85), and in some research, the bottom sub-scale level was within the dealing with stress sub-factor (46, 73). On this research, just like different research, it may be mentioned that lecturers didn’t do sufficient train. Nevertheless, issues arising from adjustments in people’ existence, particularly sedentary residing, are among the many most vital causes of persistent ailments and deaths immediately (86). Then again, it’s thought that the low common scores of lecturers on bodily exercise, in addition to dealing with stress and well being accountability, might pose a possible danger for numerous ailments, comparable to cardiovascular ailments.
The present research discovered that there was not a statistically important distinction between intercourse and the overall level of well being promotion life-style behaviors. It was discovered that male lecturers’ wholesome life-style conduct scale scores had been considerably decrease than these of feminine lecturers. The explanation for this distinction could also be associated to the cultural construction and the truth that girls have a look at points comparable to well being, diet, and aesthetics extra responsibly than males. This consequence contradicts with Kafkas et al.’s (71) research in Turkey, which discovered that there was a major distinction between intercourse knowledge and general well being promotion life-style behaviors. Tabrizi et al.’s (87) complete evaluate revealed that the outcomes of research on the significance of intercourse in health-promoting behaviors are usually not constant.
The current research discovered there was not important distinction between the intercourse and bodily exercise sub-scale. Nevertheless, male lecturers scored increased on the bodily exercise scale. This consequence matched that of Esin (88) and Baltaş (89), who reported that girls train much less. Earlier analysis has reported a major distinction between intercourse and bodily exercise. When research in Turkey and different international locations had been examined, the bodily exercise ranges of male contributors had been decided to be increased than these of feminine contributors, according to our research, though a few of them didn’t have statistical significance (37, 90, 91). Certainly, the frequency of doing sports activities or exercising amongst male lecturers was additionally discovered to be increased than that of feminine lecturers amongst secondary faculty lecturers in Austria. Dearden and Sheahan (92) discovered that girls don’t need to interact in bodily exercise, and the explanations for this are particular person, household, and social elements comparable to lack of services and gear, a protected place for strolling, and time limitation. The the explanation why male lecturers’ bodily exercise scores are considerably increased than females are: this can be as a consequence of the truth that feminine lecturers have restrictions on going out within the night as a result of such actions can normally be performed within the night after class schedules; that males have extra train alternatives within the night; and that males choose train (particularly group sports activities) to socialize and relieve stress.
The current research discovered a major distinction between the interpersonal relations sub-scale and the intercourse variable. The feminine lecturers acquired increased factors on the interpersonal relations sub-scale. The research carried out by Karakoç’s (37) discovered that feminine lecturers acquired increased scores than male lecturers within the interpersonal relations dimension, however these variations weren’t discovered to be statistically important.
Within the current research, there was not important distinction between the “well being accountability” sub-scales and intercourse. Well being accountability signifies that the person exhibits a change in perspective and conduct towards protecting behaviors, preventive behaviors, and health-promoting behaviors concerning his personal well being. It’s said that well being accountability impacts the person’s high quality of well being care (93). An vital discovering was obtained for lecturers who’re schooling employees and must be function fashions.
Within the current research, there was not statistically important distinction between the “bodily exercise,” “diet,” “non secular development,” and “stress administration” sub-scales with intercourse. Nevertheless, the scores of feminine lecturers are increased than these of male lecturers. In keeping with the present analysis’s outcomes, it may be mentioned that feminine lecturers who participated within the analysis had been extra more likely to implement well being promotion life-style behaviors exterior of bodily exercise.
On this research, there was not important distinction between lecturers’ well being promotion life-style behaviors scale, subscales, and their marital standing (p > 0.05). Nevertheless, the general common level of well being promotion life-style behaviors of married lecturers was discovered to be decrease than the common whole rating of single lecturers. According to the outcomes of the current analysis, some research in Turkey and different international locations have discovered that there’s not statistically distinction between wholesome life-style behaviors and marital standing (45, 90). Earlier research have said a major distinction between marital standing and health-promoting life-style behaviors, however this was not evidently statistically important within the current research. This consequence contradicts the outcomes of the earlier analysis. Within the research carried out by Kiliç and Çimen (90), within the sub-scale of well being accountability (p = 0.008), the bodily exercise subscale (p =0.037) was revealed to have important variations in favor of marriage. This may be defined by the truth that marriage imposes extra obligations on people, supplies important social help to spouses, and married folks lead a extra common life-style.
Within the present analysis, it was discovered that there was a statistically important distinction between lecturers who took programs on subjects associated to well being promotion by way of the well being promotion life-style behaviors scale and sub-scales. Wholesome life-style behaviors scale whole level and subscale whole level averages had been decided to be increased for lecturers who took programs on well being promotion. This result’s congruent with Kostak et al. (46) in Turkey, who reported that the well being promotion life-style behaviors scores of the first faculty instructing college students who took programs on well being promotion had been increased than these of those that didn’t take programs throughout their schooling. In one other research carried out with nursing college students, the common factors of the well being accountability and diet sub-scale and the Wholesome Way of life Behaviors Scale had been decided to be considerably increased in those that took programs on well being safety and promotion (94).
It will be important that lecturers taking health-related programs have good wholesome life-style behaviors, because it exhibits that the inclusion of well being and well being promotion programs within the faculty curriculum is environment friendly in serving to people study wholesome life-style behaviors and make them a behavior. The event of health-related behaviors usually is feasible by quitting unhealthy habits or adopting and persevering with wholesome life-style behaviors. It’s recommended that with the intention to present college students with consciousness of optimistic well being behaviors and the safety, upkeep, and improvement of well being, well being promotion points must be included extra in major faculty curricula, and practices aimed toward enhancing well being must be carried out in highschool and college curricula.
Within the present analysis, the overall well being promotion life-style behaviors rating said a statistically important distinction with lecturers’ standing of following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media (p < 0.05). It has been discovered that the overall level of lecturers who comply with wholesome life-related packages in written and visible media is increased than the overall rating of lecturers who don’t comply with them. The current research’s consequence matched that of Üçdal (49), who said that scores of general well being promotion life-style behaviors of bodily schooling lecturers confirmed a major distinction with the standing of following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media. Üçdal (49) decided that the overall rating of lecturers who comply with health-related packages is 146.4000, the overall rating of lecturers who don’t comply with well being packages is 133.0175, and the overall rating of lecturers who generally comply with well being packages is 137.3385. Nevertheless, within the research carried out by Üçdal (49), no important distinction was decided between the stress administration sub-scale and the standing of following health-related packages from the media.
In keeping with these findings, the next suggestions have been made for lecturers working in major faculties to undertake, implement, and preserve a wholesome life-style:
In-service coaching on wholesome existence must be organized in order that lecturers can undertake a wholesome life-style and apply it to their lives.
Coaching packages that present detailed details about the advantages of train and encourage train must be organized.
Lecturers, who’ve a excessive danger of regularly encountering worrying conditions must be made conscious of this case, learn how to cope successfully, and learn how to resolve the occasions.
It’s recommended that completely different scientific research be carried out by figuring out well being promotion life-style behaviors and dealing in coordination with the Ministry of Well being and the Ministry of Nationwide Schooling.
Contemplating that male lecturers largely rating excessive in train and feminine lecturers rating excessive in diet, it’s thought that it might be acceptable to create alternatives and potentialities for bodily exercise for feminine lecturers and to make plans and practices to boost consciousness amongst male lecturers about diet.
Establishing coaching packages on health-promoting life-style behaviors and making these packages part of the curriculum to unfold all through all schooling years.
4.1 Limitations and future instructions
The principle limitation of the current analysis could possibly be the truth that the pattern comprises lecturers working within the public major faculties in Amasya metropolis middle within the 2018–2019 tutorial yr. Thus, it’s recommended that different analysis be carried out to research the health-promoting life-style behaviors of lecturers at different ranges in private and non-private faculties throughout the nation.
5 Conclusion
Primarily based on the findings of this analysis, the outcomes have vital implications for lecturers working in public major faculties. Because of this research, it was revealed that the efforts of feminine lecturers working in major faculties to train weren’t adequate. It has been decided that lecturers who’re feminine, single, take programs on well being promotion, comply with packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media lead a more healthy life-style than different teams. It has been revealed that lecturers’ taking programs on well being promotion, and following packages and articles about wholesome residing in written and visible media have an effect on their wholesome life-style behaviors. Relating to the results of six parts, it was observed that the best imply rating share of well being promotion life-style behaviors was discovered for lecturers response to the non secular development part, adopted by the interpersonal relationships part, whereas lecturers’ well being promotion life-style to bodily exercise part was the bottom. In step with these outcomes, it is suggested to make plans to introduce well being promotion life-style behaviors, particularly train, to all lecturers, particularly feminine lecturers.
Information availability assertion
The unique contributions offered within the research are included within the article/supplementary materials, additional inquiries might be directed to the corresponding writer.
Ethics assertion
The research involving human contributors was authorised by the Amasya Provincial Directorate of Nationwide Schooling. The contributors offered written knowledgeable consent for participation within the research.
Creator contributions
MÖ: Conceptualization, Information curation, Formal evaluation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Mission administration, Assets, Software program, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – unique draft, Writing – evaluate & enhancing.
Funding
The writer(s) declare that no monetary help was acquired for the analysis, authorship, and/or publication of this text.
Acknowledgments
The writer want to thank all of the contributors within the research.
Battle of curiosity
The writer declares that the analysis was carried out within the absence of any business or monetary relationships that could possibly be construed as a possible battle of curiosity.
Writer’s notice
All claims expressed on this article are solely these of the authors and don’t essentially symbolize these of their affiliated organizations, or these of the writer, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that could be evaluated on this article, or declare that could be made by its producer, is just not assured or endorsed by the writer.
References
1. WHO. Alma-Ata Declaration, Worldwide Convention on Main Well being Care, Alma-Ata, USSR, 6-12 September. Geneva: WHO (1978).
Google Scholar
2. Bostan N, Beşer A. Elements affecting the wholesome life-style behaviors of nurses. J Educ Res Nurs. (2016) 14:38–44. doi: 10.5222/HEAD.2017.038
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
3. World Well being Group. Ottawa constitution for well being promotion. In: First Worldwide Well being Promotion Convention, Ottawa. Ottawa, ON: Geneva (1986).
Google Scholar
4. Levchenko V, Levchenko A. Enhancing wholesome life-style in skilled lecturers’ coaching packages in Universities of Russia. Adv Econ Bus Manag Res. (2019) 131:29–31. doi: 10.2991/aebmr.ok.200324.006
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
5. Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJL. World and regional burden of illness and danger elements, 2001. Systematic evaluation of inhabitants well being knowledge. Lancet. (2006) 367:1747–57. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68770-9
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
7. Yilmazel G, Naçar M, Çetinkaya F. Bir sanayi kuruluşunda çalişan işçilerin sagligi geliştirme davranişlari. TAF Prev Med Bull. (2015) 14:161–170. doi: 10.5455/pmb1-1410340413
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
9. Bakhtari A, Noorizade R, Poorreza A, Shojaeezadeh D, Azam Okay. The survey of life-style lady and boy college students resident in Dormitories of Tehran College of Medical Sciences. Res J Biol Sci. (2007) 2:459–61.
Google Scholar
10. Pender NJ. Well being Promotion in Nursing Follow, Norwalk, 2nd ed. Burlington, NJ: Jones & Bartlett Studying (1987), p. 57–63.
Google Scholar
11. Pender NJ. Well being Promotion in Nursing Follow, third ed. Stanford, CT: Appleton and Lange (1996).
Google Scholar
13. Pender NJ. Well being Promotion in Nursing Follow. Norwalk, CT: Appleton-Century-Crofts (1982).
Google Scholar
14. Rogers B, Kono Okay, Marziale MHP, Peurala M, Radford J, Staun J. Worldwide survey of occupational well being nurses’ roles in multidisciplinary teamwork in occupational well being providers. Office Well being Saf. (2014) 62:274–81. doi: 10.3928/21650799-20140617-03
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
15. Duran Ü, Ögüt S, Asgarpour H, Kunter D. Analysis of the well being personnel’s wholesome life-style behaviors. J Adnan Menderes Univ Well being Sci Fac. (2018) 2:138–47.
Google Scholar
16. Walker SN, Sechrist KR, Pender NJ. The well being selling life-style profile improvement and psychometric traits. Nurs Res. (1987) 36:76–80. doi: 10.1097/00006199-198703000-00002
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
17. Pender NJ, Barkauskas VH, Hayman L, Rice VH, Anderson ET. Well being promotion and illness prevention: towards excellence in nursing apply and schooling. Nurs Outlook. (1992) 40:106–12.
PubMed Summary | Google Scholar
18. Zülfünaz Ö, Teke N, Turan BG. Analysis of information attitudes and opinions of hypertension employees working in a college. Well being Care Acad J. (2020) 7:160–6.
Google Scholar
19. Upton D, Thirlaway Okay. Selling Wholesome Behaviour: A Sensible Information, 2nd ed. New York, NY: Routledge (2014), p. 76. doi: 10.4324/9781315819105
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
20. Curtin S. Traits in most cancers and coronary heart illness loss of life charges amongst adults aged 45–64: United States, 1999–2017. Natl Very important Stat Stories. (2019) 68:1–8.
PubMed Summary | Google Scholar
21. Stanaway J, Afshin A, Gakidou E, Lim S. World, regional, and nationwide comparative danger evaluation of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic dangers or clusters of dangers for 195 international locations and territories, 1990–2017: a scientific evaluation for the World Burden of Illness Research 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392:1923–94. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32225-6
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
22. Ford ES, Zhao G, Tsai J, Li C. Low-Danger life-style behaviors and all-cause mortality: findings from the nationwide well being and diet examination survey III mortality research. Am J Public Well being. (2011) 101:1922–9. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2011.300167
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
23. Zhang YB, Chen C, Pan XF, Guo J, Li Y, Franco OHet al. Associations of wholesome life-style and socioeconomic standing with mortality and incident heart problems: two potential cohort research. BMJ. (2021) 372:n604. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n604
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
24. Duran S, Çetinbaş A. The connection between wholesome life-style behaviors and physique compositions in college college students. Ankara Med J. (2021) 1:327–38. doi: 10.5505/amj.2021.92408
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
25. Akgül N. Dedication of wholesome life-style behaviors and self-efficacy-sufficiency ranges of well being personnel working in major well being care establishments in Sivas Metropolis Middle (Grasp’s thesis). Sivas: College of Cumhuriyet (2008).
Google Scholar
26. Seema D. Lecturers’ Way of life for promotion of well being in faculties. Sch Res J Interdisip Stud. (2016) 3:1752–60.
Google Scholar
27. World Well being Group. Selling Well being via Colleges. The World Well being Group’s World College Well being Initiative. Ready for WHO/HPR/HEP by S. Cohen and C. Vince Whitman, Schooling Improvement Middle, Inc., Newton, Mass., U.S.A. Geneva: World Well being Group (1996).
Google Scholar
28. T.C. MEB. Ilkögretim Ve Egitim Kanunu (5/1/1961). Kanun Numarasi: 222 Yayimlandigi R. Gazete: Tarih: 12/1/1961 Sayi: 10705 (1961).
Google Scholar
29. T.C. MEB. Ilkögretim Kurumlari Yönetmeligi, Resmi Gazete: 10.07.2010-27637 (2010).
Google Scholar
30. Çoban B, Turan M. Ögrenci görüşlerine göre superb beden egitimi ögretmeninin nitelikleri. Ölçek Geliştirme Çalişmasi Elazig, Firat Üniv Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi. (2006) 16:149–61.
Google Scholar
31. Özcebe H, Ulukol B. Saglik Hizmetlerinde Okul Sagligi Kitabi. Ankara: Yücel Ofset. (2008)
Google Scholar
32. Yener FÖ. The significance of directors and lecturers’ function mannequin behaviours on the options of scholars’ unfavorable acts (Grasp’s thesis). Kocaeli: Kocaeli College of Kocaeli (2011).
Google Scholar
33. Tokuç B, Berberoglu U. Well being selling existence amongst major faculty lecturers working in Edirne. TAF Prev Med Bull. (2007) 6:421–6.
Google Scholar
34. Faught EL, Gleddie D, Storey KE, Davison CM, Veugelers PJ. Wholesome life-style behaviours are positively and independently related to tutorial achievement: an evaluation of self-reported knowledge from a nationally consultant pattern of Canadian early adolescents. PLoS ONE. (2017) 12:e0181938. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181938
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
35. Wilf-Miron R, Kittany R, Saban M, Kagan I. Lecturers’ traits predict college students’ steerage for wholesome life-style: a cross-sectional research in Arab-speaking faculties. BMC Public Well being. (2022) 22:1420. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13795-5
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
36. Znyk M, Kaleta D. Wholesome life-style counseling, and boundaries perceived by basic practitioners in Poland. Entrance Public Well being. (2023) 11:1256505. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1256505
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
37. Karakoç A. Wholesome life-style behaviors of classroom lecturers and willpower of some elements affecting these behaviors (Grasp’s thesis). Sivas: College of Cumhuriyet (2006).
Google Scholar
38. Ak Ş, Çelen Ü, Özen Y, Tabak RS, Piyal B. Well being behaviours of the personnel of major faculties in ANKARA. TAF Prev Med Bull. (2006) 5:83–93.
Google Scholar
39. Gürel FS, Gemalmaz A, Dişçigil G. Bir grup ilkögretim ögretmeninin beslenme hakkindaki bilgi düzeyleri, bilgi kaynaklari ve fiziksel aktivite durumlari. ADÜ Tip Fakültesi Dergisi. (2004) 5:21–6.
Google Scholar
40. Kabataş MS, Kizil H, Duman D. Bayan ögretmenlerin meme kanserive kendikendine meme muayenesi hakkinda bilgi tutum ve davranişlarinin incelenmesi. Meme Sagligi Dergisi. (2010) 6:150–5.
Google Scholar
41. Güner IC, Demir F. The willpower of the well being promotion life type of working room nurses. J Nursol. (2006) 9:17–25.
Google Scholar
42. Bakhtari A, Noorizade R, Poorreza, A, Shojaeezadeh D, Azam Okay. The survey of life-style lady and boy college students resident in Dormitories of Tehran College of Medical Sciences. Res J Biol Sci. (2007) 2:459–61.
Google Scholar
43. Ghaffari Nejad AR, Pouya F. Self selling behaviors amongst lecturers in Kerman. J Guilan Univ Med Sci. (2002) 11:1–9.
Google Scholar
44. Hill J, Draper CE, De Villiers A, Fourie JM, Mohamed S, Parker W, et al. Selling wholesome life-style behaviour via the life-orientation curriculum: lecturers’ perceptions of the healthkick intervention. S Afr J Educ. (2015) 35:1–9. doi: 10.15700/201503070003
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
45. GudŽinskiene V, Cesnavičiene J. Lecturers‘ data of well being and wholesome life-style as a precondition for the event of the wholesome life-style of pupils. Soc Work. (2013) 12:121–36.
Google Scholar
46. Kostak MA, Kurt S, Süt N, Akarsu Ö, Ergül GD. Wholesome life-style behaviors of nursing and classroom instructing college students. TAF Prev Med Bull. (2014) 13:189–96. doi: 10.5455/pmb.1-1362174271
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
47. Pirzadeh A, Sharifirad G, Kamran A. Wholesome life-style in lecturers. J Educ Well being Promot. (2012) 1:1–27. doi: 10.4103/2277-9531.104816
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
48. McNamara R, Quinn R, Murrin C, Bel-Serrat S. Lecturers’ views on the boundaries to wholesome life-style behaviors amongst adolescent women of deprived backgrounds in Eire: a qualitative research. Urge for food. (2021) 167:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2021.105585
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
49. Üçdal Ç. The analysis of bodily schooling lecturers wholesome life type behaviors: erzurum province pattern (Grasp’s thesis). Erzurum: College of Atatürk (2019).
Google Scholar
51. Craft BJ, Grasser C. The connection of recipprocity to self well being care in older girls. J Ladies Getting old. (1998) 10:35–47. doi: 10.1300/J074v10n02_04
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
52. Gray M, Berry D, Davidson M, Galasso P, Gustafson E, Melkus G. Preliminary testing of a program to forestall sort 2 diabetes amongst excessive danger youth. J Sch Well being. (2004) 74:10–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1746-1561.2004.tb06595.x
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
54. Satio YA, Prather CM, Van Dyke CT, Fett S, Zinsmeister AR, Locke GR. Results of multidisciplinary schooling on outcomes in sufferers with irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2004) 2:576–84. doi: 10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00241-1
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
56. Carlson ED. A case research in translation methodology utilizing the well being selling life-style profile II. Public Well being Nurs. (2000) 17:61–70. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1446.2000.00061.x
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
57. Bailey RR, Phad A, McGrath R, Debra Haire-Joshu D. Prevalence of 5 life-style danger elements amongst U.S. adults with and with out stroke. Disabil Well being J. (2019) 12:323–7. doi: 10.1016/j.dhjo.2018.11.003
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
58. Bagwell MM, Bush HA. Well being conception and professional movement in blue collar employees: program planning points. Am Assoc Occup Well being Nurs J. (1999) 47:512–8. doi: 10.1177/216507999904701102
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
59. Beşer A, Bahar Z, Büyükkaya D. Well being selling behaviors and elements associated to life-style amongst Turkish employees and occupational well being nurses’ obligations of their well being selling actions. Ind Well being. (2007) 45:151–9. doi: 10.2486/indhealth.45.151
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
60. Kamwendo Okay, Faresjo MT, Gustavsson U, Jansson M. Adherence to wholesome existence a comparability of nursing and physiotherapy college students. Adv Physiother. (2000) 2:63–74. doi: 10.1080/140381900443328
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
61. Karasar N. Scientific Analysis Technique: Ideas Rules Methods, thirty sixth ed. Ankara: Nobel Yayinevi (2023).
Google Scholar
62. Walker SN, Hill-Polerecky DM. Psychometric Analysis of the Well being Selling Way of life Profile II. Omaha, NE: College of Nebraska Medical Middle (1996).
Google Scholar
63. Bahar Z, Beşer A, Gördes N, Ersin F, Kissal A. Wholesome life type conduct scale II: a reliability and validity research. Cumhuriyet Nurs J. (2008) 12:1–13.
Google Scholar
64. Nunnally JC. Psychometric Principle, 2nd ed. New York, NY: McG-raw-Hill (1978).
Google Scholar
65. Büyüköztürk S, Çakmak KE, Akgün EÖ, Karadeniz S, Demirel F. Scientific Analysis Strategies, fifteenth ed. Ankara: Pegem Akademi (2010) p. 85–6.
Google Scholar
66. Discipline A. Discovering Statistics Utilizing SPSS and Intercourse and Medication and Rock ‘n’ Roll, third ed. London: SAGE Publications (2009), p. 19.
Google Scholar
67. Altun I. A research on health-related attitudes and well being life-style behaviors of the folks residing in Kocaeli. Saglik Toplum. (2002) 3:41–51.
Google Scholar
68. Karadeniz G, Yanikekrem Uçum E, Dedeli Ö, Karaagaç Ö. Well being life-style behaviors of college college students. TAF Prev Med Bull. (2008) 7:497–502.
Google Scholar
69. Güler G, Güler N, Kocataş S, Yildirim F, Akgül N. Behaviors of wholesome life type of educational personnel who work at a college. Cumhuriyet Nurs J. (2008) 12:18–26.
Google Scholar
70. Yilmaz Okay. An examination of the correlation between wholesome life-style behaviors in younger horse riders and anthropometric measurements and cardiopulmonary parameters (Grasp’s thesis). Bursa: College of Uludag (2020).
Google Scholar
71. Kafkas ME, Sahin Kafkas A, Acet M. Evaluation of bodily schooling lecturers’ stage of wholesome life type behavious. Dumlupinar Unii J Soc Sci. (2012) 32:47–56.
Google Scholar
72. Kaya F, Ünüvar R, Biçak A, Yorganci E, Çinar B, Öz F, et al. Analyzing the well being promotion behaviors of school members and affecting elements. Türk Silahli Kuvvetleri Koruyucu Hekimlik Bül. (2008) 7:59–64.
Google Scholar
73. Çebi M. Examination of the wholesome life kind behaviours of athletes. Inonu Univ J Phys Educ Sport Sci. (2018) 5:13–20.
Google Scholar
74. Rahnavard Z, Zolfaghari M, Kazemnejad A, Zarei L. The relation between feminine youngsters’ life type and osteoporosis prevention. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. (2006) 12:53–61.
Google Scholar
75. Alzahrani SH, Malik AA, Bashawri J, Shaheen SA, Shaheen MM, Alsaib AA, et al. Well being-promoting life-style profile and related elements amongst medical college students in a Saudi college. SAGE Open Med. (2019) 7:1–7. doi: 10.1177/2050312119838426
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
76. Geok SK, Yusof A, Lam SK, Japar S, Leong OS, Fauzee SOM. Bodily exercise and health-promoting life-style of pupil nurses in Malaysia. J Biosci Med. (2015) 3:78–87. doi: 10.4236/jbm.2015.33012
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
77. Gore MN, Menon KC, Safai AA, Shukla S, Yeravdekar R. Determinants of health-promoting existence amongst Indian College college students. Int J Well being Promot Educ. (2020) 59:1–10. doi: 10.1080/14635240.2020.1726202
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
78. Paudel S, Bahadur KGC, Bhandari DB, Bhandari L, Arjyal A. Well being associated life-style behaviors amongst undergraduate medical college students in patan academy of well being sciences in Nepal. J Biosci Med. (2017) 5:43–53. doi: 10.4236/jbm.2017.59005
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
79. Özbek Z. Defining wholesome life-style behaviours of nurses (Grasp’s. Thesis). Gaziantep: Gaziantep College (2019).
Google Scholar
80. Yilmaz D, Arkan B, Cinar HG. Analyzing the connection between the wholesome life-style behaviours, anthropometric measurements and cardiovascular features of first grade college college students. Oxid Commun. (2016) 39:3038–49.
Google Scholar
81. Yilmaz D, Yilmaz Okay, Goncagül G. Examination of the connection between bodily exercise ranges and wholesome life-style behaviors of college college students. Asian Pac J Well being Sci. (2017) 4:30–3. doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2017.4.4.8
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
82. Al-Kandari F, Vidal VL. Correlation of the health-promoting life-style, enrollment stage, and tutorial efficiency of School of Nursing college students in Kuwait. Nurs Well being Sci. (2007) 9:112–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2018.2007.00311.x
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
83. Gömleksiz M. Wholesome life type behaviours of medical school college students and associated elements (Grasp’s thesis). Elazig: College of Firat (2019).
Google Scholar
84. Safaie N, Ketabi S, Kia N, Mirmohammadkhani M, Moonesan MR, Paknazar F. Exploration of psychological well being issues in affiliation with health-promoting life-style profile in Iranian medical college students: a cross-sectional research. J Educ Well being Promot. (2020) 9:84. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_582_19
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
85. Simşek H, Öztoprak D, Ikizoglu E, Safali F, Yavuz Ö, Onur Ö, et al. Wholesome life-style behaviours and associated elements of medical faculty college students. DE Tip Fakültesi Dergisi. (2012) 26:151–7.
Google Scholar
86. Kaminsky LA, German C, Imboden M, Ozemek C, Peterman JE, Brubaker PH. The significance of wholesome life-style behaviors within the prevention of heart problems. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. (2022) 70:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2021.12.001
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
87. Tabrizi JS, Doshmangir L, Najibeh Khoshmaram N, Elham Shakibazadeh E, Hosein Mashhadi Abdolahi HM, Roghayeh Khabiri R. Key elements affecting well being selling behaviors amongst adolescents: a scoping evaluate. BMC Well being Serv Res. (2024) 24:58. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-10510-x
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
88. Esin N. Dedication and improvement of well being behaviors of commercial employees (Ph.D. thesis). Istanbul: Istanbul College (1997).
Google Scholar
89. Baltaş Z. A preliminary research on buying well being conduct, well being conduct patterns of the Turkish neighborhood residing in England. In: Proceedings of the Vth Nationwide Convention on Public Well being. Istanbul (1996).
Google Scholar
90. Kiliç L, Çimen Okay. Analysis of the wholesome life-style behaviors of bodily schooling lecturers. Eur J Phys Educ Sport Sci. (2017) 3:317–28. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.111508
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
91. Lee RLT, Loke AJTY. Well being-promoting behaviors and psychosocial well-being of college college students in Hong Kong. Public Well being Nurs. (2005) 22:209–20. doi: 10.1111/j.0737-1209.2005.220304.x
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
92. Dearden J, Sheahan S. Counseling middle-aged girls about bodily exercise utilizing the stage of change. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. (2002) 14:492–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7599.2002.tb00081.x
PubMed Summary | Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
93. Lusk SL, Kerr MJ, Ronis DL. Check of well being promotion mannequin as a causal mannequin of employee’s use of listening to safety. Nurs Res. (1994) 43:151–7. doi: 10.1097/00006199-199405000-00005
Crossref Full Textual content | Google Scholar
94. Ayaz S, Tezcan S, Akinci F. Well being promotion conduct of nursing faculty college students. Cumhuriyet Nurs J. (2005) 9:26–34.
Google Scholar


