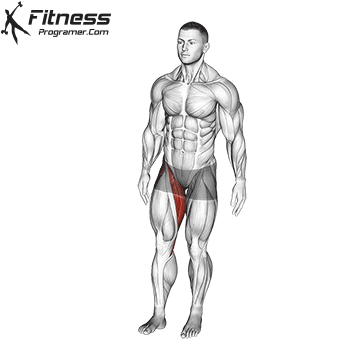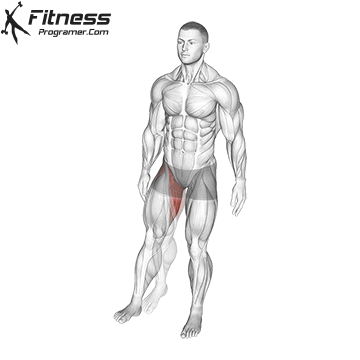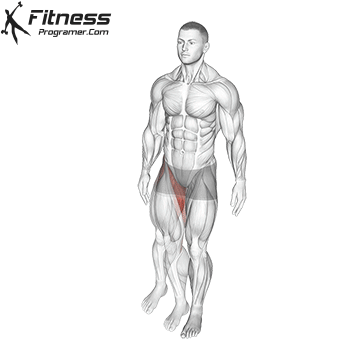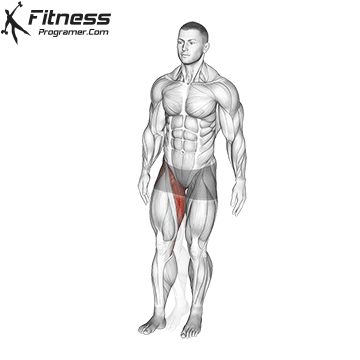
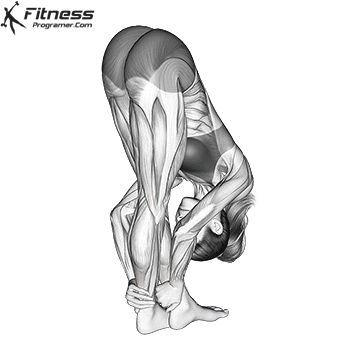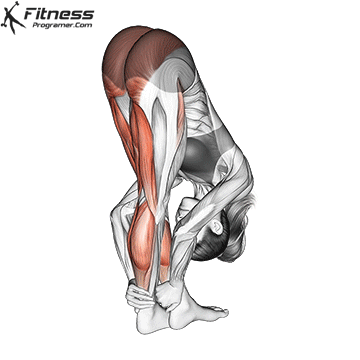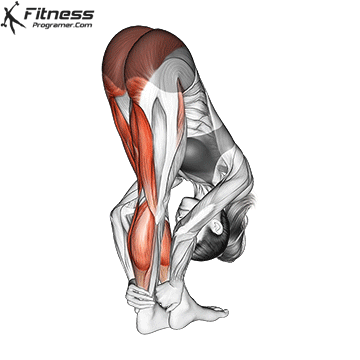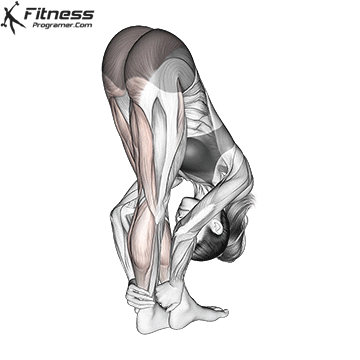
The hamstrings are a bunch of three massive muscle mass situated on the posterior compartment of the thigh. They span each the hip and knee joints, taking part in a significant function in decrease physique motion, together with strolling, operating, squatting, and stabilizing the pelvis. This text supplies a science-backed breakdown of the hamstring group’s anatomy, biomechanics, widespread accidents, and coaching methods to enhance efficiency and reduce danger.
The Three Hamstring Muscle tissue
The hamstring group consists of:
- Biceps Femoris (lengthy and quick head)
- Semitendinosus
- Semimembranosus
These muscle mass originate from the ischial tuberosity of the pelvis (besides the quick head of the biceps femoris, which originates on the femur) and insert under the knee on the tibia or fibula. They’re biarticular muscle mass, that means they cross each the hip and knee joints.
1. Biceps Femoris
- Lengthy Head Origin: Ischial tuberosity (pelvis)
- Brief Head Origin: Linea aspera of the femur
- Insertion: Head of the fibula
- Operate:
- Knee flexion
- Lateral rotation of the leg when the knee is flexed
- Hip extension (lengthy head solely)
2. Semitendinosus
- Origin: Ischial tuberosity (pelvis)
- Insertion: Medial floor of the proximal tibia (a part of the pes anserinus)
- Operate:
- Knee flexion
- Medial rotation of the leg when the knee is flexed
- Hip extension
3. Semimembranosus
- Origin: Ischial tuberosity (pelvis)
- Insertion: Posterior floor of the medial tibial condyle
- Operate:
- Knee flexion
- Medial rotation of the leg
- Hip extension
Capabilities of the Hamstrings Muscle Group
The hamstrings serve a number of key capabilities in locomotion and stability:
- Hip Extension: Very important for sprinting, leaping, and rising from a seated place.
- Knee Flexion: Required for operating, squatting, and deceleration.
- Posterior Pelvic Tilt: Assists in stabilizing the pelvis and backbone.
- Eccentric Management: Throughout operating, particularly within the late swing section, hamstrings decelerate the forward-moving tibia, stopping overextension.
Prepare the Hamstrings Successfully
A balanced hamstring program consists of each:
- Hip-dominant workout routines (concentrating on hip extension)
- Knee-dominant workout routines (concentrating on knee flexion)
High Compound Workouts:
These interact the hamstrings together with glutes and different posterior chain muscle mass.
High Isolation Workouts:
Isolation workout routines are perfect for muscle development and correcting imbalances.
Quantity and Depth Pointers
- Frequency: 2–3x per week
- Reps:
- Hypertrophy: 8–12 reps
- Energy: 3–6 reps
- Endurance: 12–20 reps
- Units: 3–5 per train
- Relaxation: 60–120 seconds relying on objective
Coaching Suggestions
- Eccentric Emphasis: Incorporate workout routines that concentrate on the lengthening section to reinforce muscle resilience.
- Glute Activation: Make sure the glutes are engaged to help hip extension actions.
- Unilateral Actions: Embody single-leg workout routines to handle imbalances and enhance stability.
- Type and Approach: Prioritize correct kind to maximise effectiveness and scale back damage danger.
Muscle Activation Issues
Workouts like Kettlebell Swings, Nordic Hamstring Curls and Romanian Deadlifts have been proven to elicit excessive ranges of hamstring activation. Emphasizing a full vary of movement and managed eccentric phases can result in vital energy and hypertrophy good points.
Hamstrings and Athletic Efficiency
Strong hamstring muscle mass are integral to varied athletic endeavors:
- Sprinting: Facilitate highly effective hip extension and knee flexion.
- Leaping: Contribute to explosive take-offs and managed landings.
- Directional Modifications: Help in agility and fast transitions.
- Lifting: Help actions like deadlifts and squats by stabilizing the posterior chain.
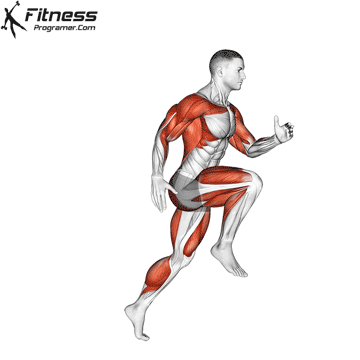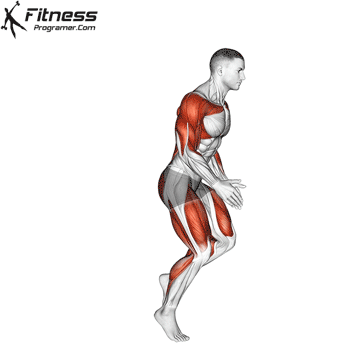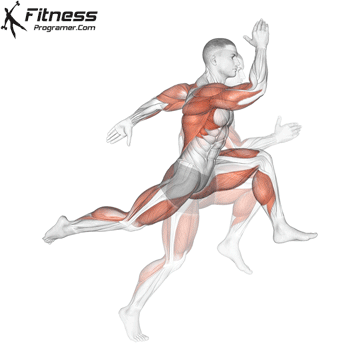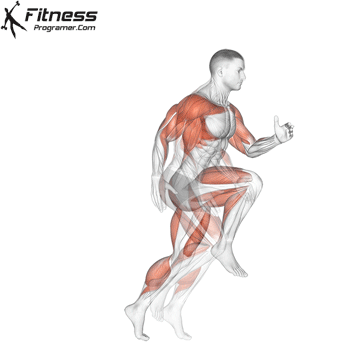
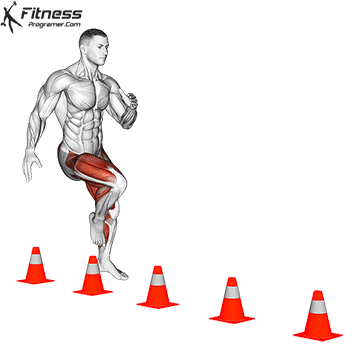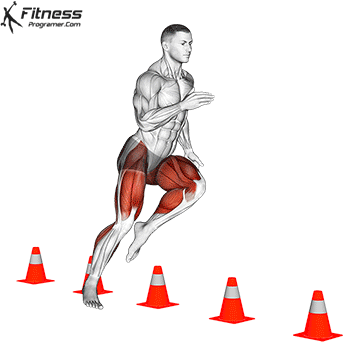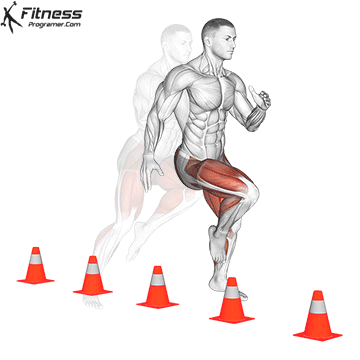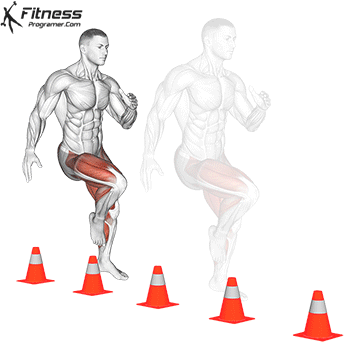
Widespread Hamstring Accidents
Hamstring accidents are among the many commonest in sports activities. Understanding the kinds, causes, and danger elements is important for prevention.
1. Strains (Pulled Hamstring)
- Grades:
- Grade I: Delicate overstretching
- Grade II: Partial tear
- Grade III: Full rupture
- Causes: Sudden acceleration or deceleration, inadequate warm-up, poor flexibility, muscle imbalances.
2. Tendinopathy
- Proximal hamstring tendinopathy (PHT) happens on the ischial tuberosity and is widespread in runners and athletes with extended sitting or repetitive hip flexion.
3. Avulsion Accidents
- Happens when the tendon pulls away from the bone, generally taking a chunk of bone with it. Commonest in adolescents and athletes underneath excessive pressure hundreds.
Threat Elements
- Earlier hamstring damage
- Poor eccentric energy
- Fatigue and overtraining
- Muscle imbalances (e.g., quad dominance)
- Improper biomechanics
Prevention Suggestions:
- Progressive Overload: Steadily improve coaching depth to permit adaptation.
- Dynamic Heat-Ups: Put together the muscle mass for exercise by movement-based stretching.
- Flexibility Coaching: Incorporate static and dynamic stretches to keep up muscle elasticity.
- Strengthening Workouts: Give attention to each concentric and eccentric actions to construct resilience.
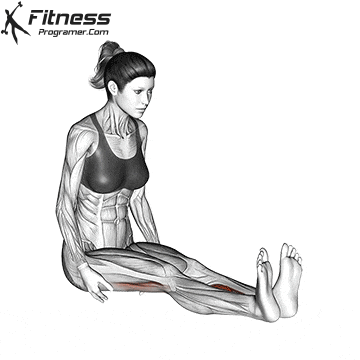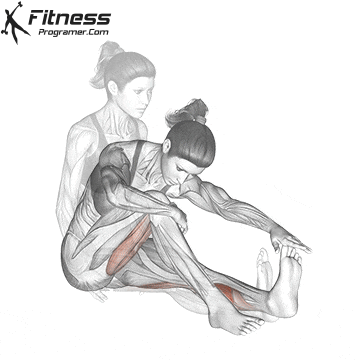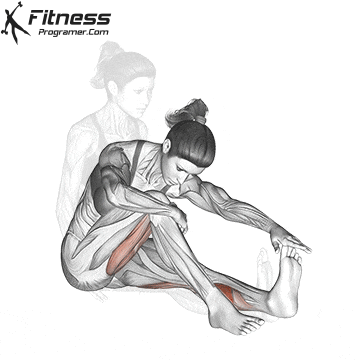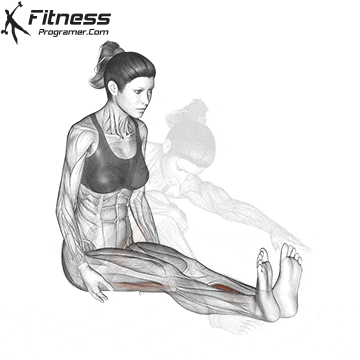
When to Search Medical Assist
Search skilled analysis in case you expertise:
- Sudden sharp ache behind the thigh
- Swelling, bruising, or incapacity to stroll
- Power tenderness close to the sit bone
- Recurrent strains regardless of correct coaching
Key Takeaways: Why the Hamstrings Matter
- The hamstrings play a essential function in decrease physique motion, stability, and athletic efficiency.
- Balanced coaching that features each energy and adaptability parts is important.
- Preventative measures, together with correct warm-ups and progressive coaching, can mitigate damage dangers.
- Understanding the anatomy and performance of the hamstrings can inform efficient coaching and rehabilitation methods.
References
- Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. eighth ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2017.
- Opar DA, Williams MD, Defend AJ. Hamstring pressure accidents: elements that result in damage and re-injury. Sports activities Med. 2012;42(3):209-226.
- Bourne MN, et al. Impact of eccentric train on hamstring structure. Br J Sports activities Med. 2017;51(5):369–377.
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Hamstring Damage Information
- McCall A, et al. Threat elements, testing and prevention of hamstring accidents in skilled soccer. Br J Sports activities Med. 2014;48(2):135–136.
- Biceps Femoris Activation throughout Hamstring Energy Workouts: A Systematic Evaluation
- van Dyk, N., Behan, F.P., & Whiteley, R. (2019). Together with the Nordic hamstring train in damage prevention programmes halves the speed of hamstring accidents: a scientific assessment and meta-analysis of 8459 athletes. British Journal of Sports activities Drugs, 53(21), 1362–1370. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2018-100045


